Maintaining the health of your dog is a multifaceted task that goes beyond the common concerns of diet and exercise. One often-overlooked aspect is dental health, specifically the risk of cavities—essentially holes in teeth caused by decay. While cavities are more synonymous with human dental health, they can affect dogs too, leading to pain, infection, and overall decline in quality of life. This article seeks to explore the nature of dental caries in dogs, the symptoms to watch for, preventative measures, and treatment options.
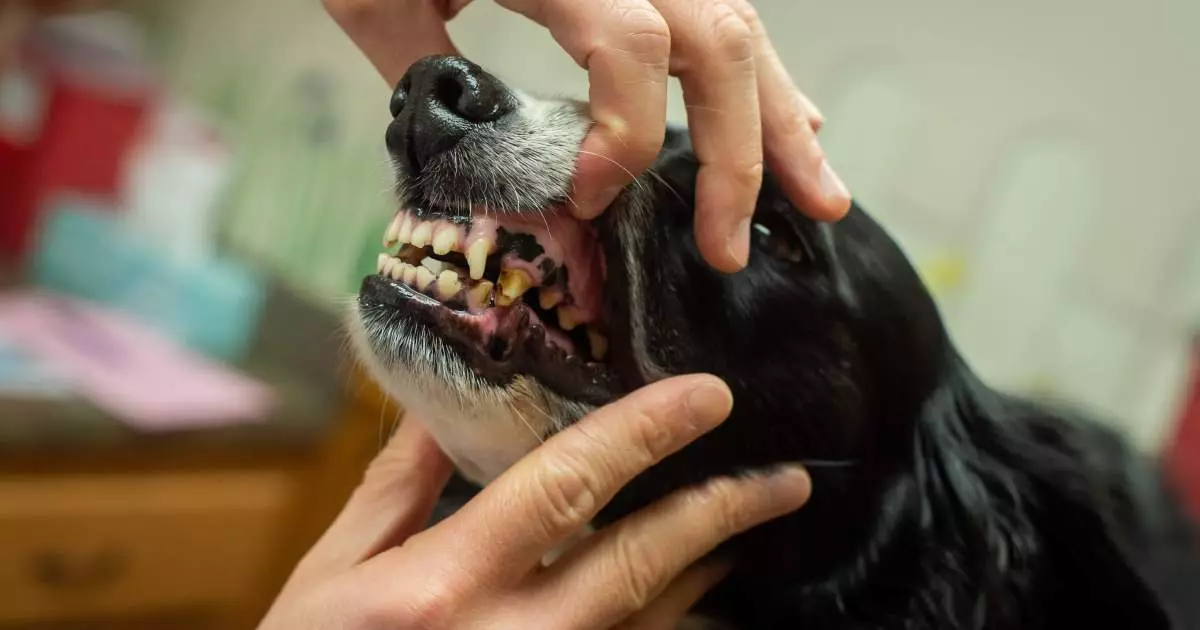
Many pet owners may not realize that their canine companions can suffer from dental cavities. The initial stages of cavity development can be asymptomatic, making it difficult to detect until the condition worsens. Some signs that could indicate the presence of cavities in your dog include:
– Visible Holes or Discoloration: Look for dark spots or noticeable holes on your dog’s teeth.
– Bad Breath: Persistent foul odor can be a clear indication of dental issues.
– Excessive Drooling: An increase in saliva production can signal discomfort.
– Eating Difficulty: If your dog seems reluctant to chew or shows signs of pain while eating, it could be due to dental pain.
– Pawing or Rubbing at the Mouth: Dogs may use their paws to alleviate discomfort, thus drawing attention to their mouths.
– Swollen or Bleeding Gums: Red or inflamed gums can be a direct sign of oral disease and cavities.
If you observe any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek veterinary care promptly.
Dental cavities in dogs develop as a result of plaque accumulation, which starts with bacteria forming a sticky layer on the teeth. As plaque hardens into tartar, it becomes increasingly difficult to remove. This bacteria produces harmful acids that erode the tooth’s protective layers, leading to cavities over time. Several factors contribute to the likelihood of a dog developing dental caries:
– Diet: Foods high in carbohydrates and sugars can exacerbate the formation of cavities. While many commercial dog foods aim to minimize this risk, certain treats may still pose challenges.
– Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing is essential for preventing plaque build-up. Ignoring dental care can lead to substantial risks.
– Genetics: Certain breeds are predisposed to dental issues due to the alignment and structure of their teeth. Smaller breeds often face an increased risk due to overcrowding.
– Health Conditions: Dogs with diseases such as diabetes can have altered immunity, making dental problems more likely.
– Age: As dogs age, the wear and tear on their teeth can increase their susceptibility to cavities.
– Saliva Composition: Variations in saliva can influence how effectively a dog resists plaque and cavity formation.
Understanding these causes is crucial for any dog owner aiming to prevent dental issues in their pets.
If you suspect your dog has a cavity, a comprehensive dental examination by a veterinarian is necessary. This examination often includes X-rays to assess the extent of the decay and determine the best course of action.
Upon diagnosis, the treatment plan may involve:
– Professional Dental Cleaning: A thorough cleaning to remove tartar and plaque buildup, usually performed under anesthesia. This helps to prevent new cavities from developing.
– Fillings: For cavities caught early, fillings can restore the tooth’s structure, similar to human dental care.
– Root Canal Therapy: In more severe cases where decay has reached the inner pulp, this procedure involves cleaning out infected tissue and sealing the tooth to prevent further infection.
– Tooth Extraction: If the cavity is too severe to treat, the veterinarian may recommend extraction to prevent further pain and complications.
Costs for these procedures can vary significantly, influenced by geographical location, specific treatments, and the severity of the condition. Basic treatments may range from a few hundred dollars to over a thousand for intricate care like root canals.
The best strategy for managing your dog’s dental health is prevention. Here are key practices to incorporate into your dog care routine:
– Regular Brushing: Use dog-specific toothpaste and brush your dog’s teeth several times a week or even daily.
– Balanced Diet: Provide nutritious food with low sugars and carbohydrates to reduce plaque formation.
– Dental Chew Toys: These can help mechanically clean teeth and promote healthy gums.
– Water Additives: Consider using dental-specific additives that help neutralize plaque when mixed with water.
– Routine Veterinary Check-ups: Regular professional cleanings and vet consultations help in spotting dental problems early.
While the implications of dental health in dogs are often underestimated, understanding and addressing the risk of cavities can significantly enhance your pet’s quality of life. Being vigilant about signs, practicing good dental hygiene, and consulting with a veterinarian can prevent serious issues in your furry companion. Always explore tailored dental care practices suited for your dog’s specific needs to ensure a happy and healthy life together.