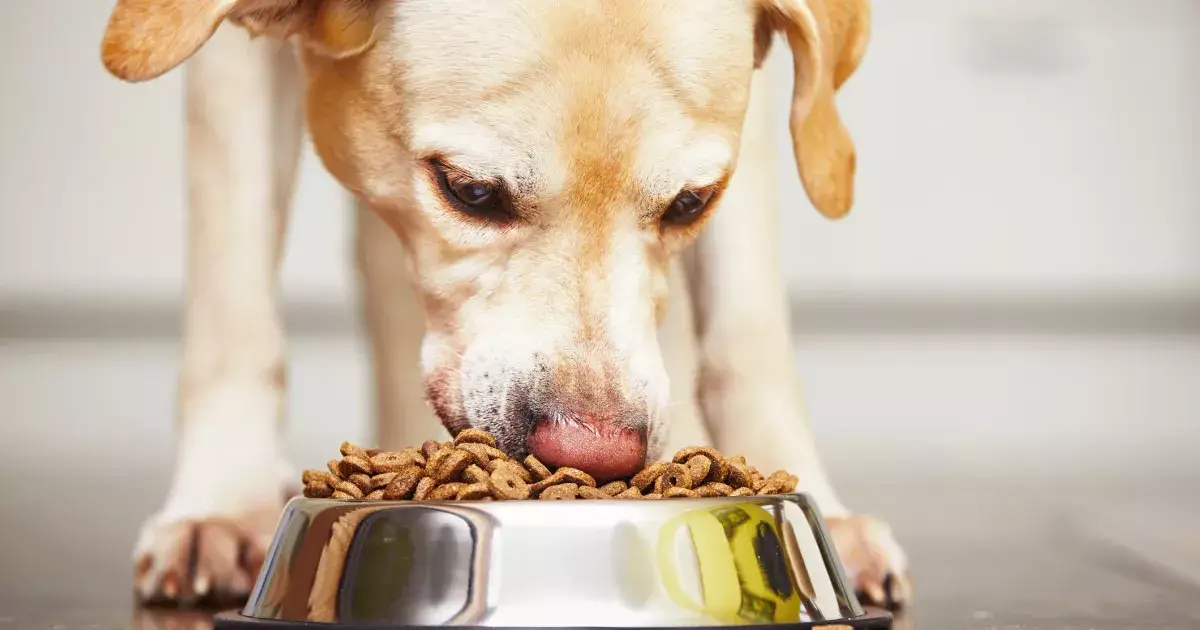
The narrative surrounding dog nutrition is changing rapidly as more pet owners begin to question the conventional norm of feeding dogs exclusively processed foods. For decades, the majority of dog owners turned to kibble and commercial dried food, trusting that these products met all their pets’ dietary requirements. However, a growing awareness regarding the quality of ingredients and the health implications of processed food is triggering a significant transformation in pet nutrition. This article will explore the reasons behind this shift, the benefits of integrating whole foods into a dog’s diet, and practical steps pet parents can take to improve their furry companions’ nutrition.
When examining processed dog foods, it is crucial to consider the processing methods these products undergo. Often, commercial pet food is subjected to extreme processing techniques designed to enhance shelf life and palatability, but these methods frequently come at the expense of nutritional value. Ingredients in these commercial diets may include meat by-products, low-grade fillers, and synthetic additives all of which degrade the quality of the food.
The ingredients listed on the packaging can also be misleading. Pet foods marketed as “high-quality” may still contain subpar elements that do not provide any nutritional benefits for dogs. This lack of transparency leaves pet owners in complicated predicaments, often unsure of what they are actually feeding their pets. For many canine companions, this diet could result in serious health complications over time as reliance on processed foods does not usually fulfill their nutritional needs.
Veterinarians and canine nutritionists increasingly advocate for diets that consist of whole, unprocessed foods, and pet owners are starting to take notice. The benefits of such diets are well-supported by research and anecdotal evidence alike. Whole foods—those that are minimally processed and devoid of artificial ingredients—offer numerous advantages including richer nutritional profiles, better ingredient quality, and reduced risk of allergens.
One of the primary benefits of feeding a dog a whole food diet is the comprehensive array of essential nutrients it can provide. Unlike processed foods that and formulated to be “complete,” whole foods display naturally occurring levels of proteins, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals that promote overall canine health. These nutrients are crucial for maintaining good health and preventing chronic disease.
Opting for whole, unprocessed ingredients can significantly impact a dog’s health. For instance, digestive issues are among the most common health problems faced by dogs consuming processed diets. These issues often stem from indigestible fillers and artificial additives found in commercial pet foods. By incorporating whole foods—such as meats, vegetables, and fruits—to their diets, pet owners can promote healthy digestion, encourage a balanced microbiome, and decrease the likelihood of gastrointestinal problems.
Additionally, a whole food diet aids in weight management. The high-calorie, low-fiber nature of processed foods often leads to obesity in pets, a condition that can cause myriad health complications. Whole foods, rich in fiber and balanced in a variety of nutrients, help to keep dogs satiated and promote a healthy weight.
Furthermore, dental health is another area where whole foods can make a substantial difference. Many processed foods are soft, lacking the crunchy texture that helps mechanically clean a dog’s teeth. Whole foods, particularly raw vegetables, provide a natural cleaning action, helping to reduce tartar buildup and promote better dental hygiene.
For pet owners looking to shift their dog’s diet away from processed foods, taking small, gradual steps is essential. Begin by incorporating small amounts of whole foods into their existing diet. Options like cooked sweet potatoes, green beans, or lean meats are not only safe but also beneficial. Consulting with a veterinarian can provide tailored dietary advice, particularly for dogs with specific health concerns.
Moreover, educating yourself about human-grade dog foods can lead to improved nutrition for your pet. The conversation about the relevance of whole foods versus processed options is vibrant in pet care communities, with many owners sharing their experiences and knowledge about feeding their dogs a less processed diet.
The push towards whole foods in canine diets is gaining momentum, supported by increasing awareness regarding the impact of processing on nutritional value. By prioritizing high-quality ingredients and reducing reliance on processed foods, pet owners can substantially improve their dogs’ health, well-being, and quality of life.