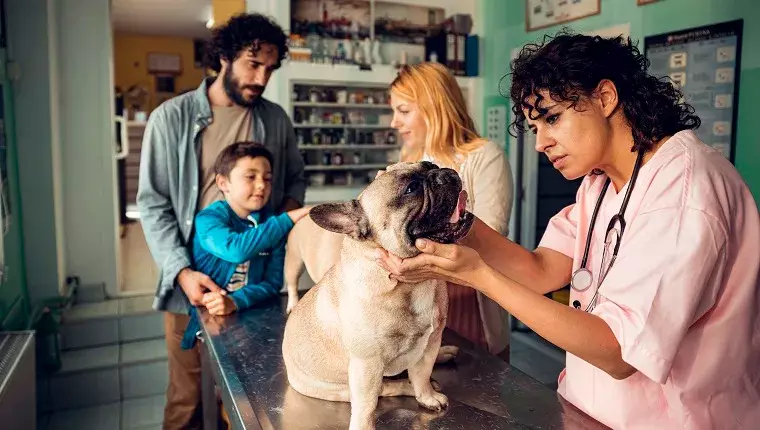
Abnormal molar development in dogs is a pressing health concern primarily seen in smaller breeds. This dental anomaly, specifically identified as dilacerated mandibular first molar, occurs when there isn’t enough space for the molars to grow correctly. It impacts not only the dog’s dental health but also their overall well-being, leading to a myriad of symptoms that can be distressing for both the pet and its owner.
Identifying signs of abnormal molar development early on is crucial. Pet owners should be vigilant for symptoms that may suggest oral health issues in their dogs. Common indicators include receding gums, inflamed or bleeding gums, pain while eating, and a noticeable decrease in appetite. These symptoms are often accompanied by behavioral changes, as the discomfort can lead dogs to become irritable or withdrawn. A thorough assessment of your dog’s oral health can reveal the severity of the issue, making it vital to monitor their condition closely.
The root causes of abnormal molar development vary, but they typically stem from insufficient room for proper dental formation. This lack of space may lead to teeth emerging at unnatural angles or being positioned in unexpected areas. Additionally, physical trauma to the mouth can trigger or exacerbate these dental issues. Certain dog breeds, such as Boston Terriers, French Bulldogs, and Pugs, are predisposed to developing these types of dental conditions due to their unique jaw structures. Understanding breed-specific vulnerabilities can help pet owners take preventive measures or seek prompt treatment when necessary.
If there’s a suspicion that a dog is experiencing abnormal molar development, a visit to the veterinarian is essential. The diagnosis process typically involves a thorough physical examination, an oral check-up, and inquiries about any recent injuries that the dog may have sustained. To confirm their findings, veterinarians often utilize dental X-rays to get a clearer picture of the teeth and their positioning. This comprehensive assessment allows the vet to understand the extent of the problem and formulate an effective treatment plan.
Treatment for abnormal molar development varies based on the severity of the condition. In some cases, pain management strategies may be implemented, along with the potential extraction of affected teeth. Following any surgical intervention, adherence to prescribed medication and careful monitoring of recovery are critical for the dog’s well-being. Offering a modified diet can also help prevent discomfort during meal times, giving the dog a more enjoyable eating experience during their recovery.
Abnormal molar development can significantly impact a dog’s quality of life. Therefore, recognizing the signs and seeking immediate veterinary care are essential for effective treatment. Pet owners should remain proactive about their dog’s dental health, ensuring they receive regular check-ups and addressing any emerging issues promptly. Taking these steps can help prevent the condition from worsening, allowing dogs to lead healthier and happier lives.