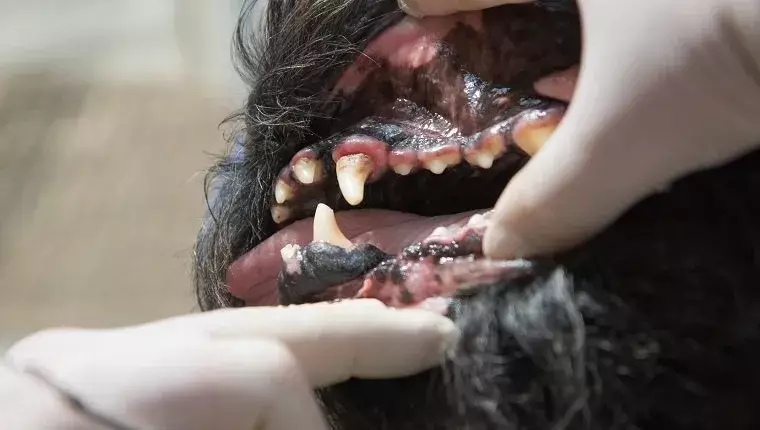
Gingivitis in dogs represents a significant health concern, marked primarily by inflammation of the gums. It serves as the preliminary phase of more severe gum diseases, primarily periodontal disease. While many pet owners may underestimate the importance of their dog’s dental hygiene, gingivitis is not merely a cosmetic issue — it is a preventable and treatable condition. If ignored, however, it can progress to advanced stages, culminating in tooth loss and even systemic health problems affecting vital organs.
Detecting gingivitis in dogs necessitates vigilance from pet owners. Initial symptoms often present as a subtle redness or swelling of the gums. As the condition worsens, indicators become increasingly pronounced. Common symptoms that may signal the presence of gingivitis include:
– Inflammation and redness along the gumline
– Noticeable swelling of the gums
– Halitosis, or bad breath, stemming from bacterial growth
– Presence of plaque, identifiable as stained teeth
– Tartar buildup, characterized by hardened deposits
– Gums that bleed during brushing or other minor agitation
– Pus discharge from the gums upon contact
– Signs of discomfort, such as difficulty chewing or reluctance to eat
– Increased drooling and loose teeth
– Receding gums that expose more of the tooth roots
Acknowledging these signs early and approaching a veterinarian can significantly impact treatment outcomes.
The primary culprits for gingivitis in dogs derive from dietary habits and inadequate oral care. Factors that heighten a dog’s risk for developing gum disease include:
– A diet deficient in proper nutrients or high in sugars
– Insufficient routine dental care
– Crowded teeth, particularly in smaller breeds
– Self-grooming habits that might inadvertently harm oral integrity
When food particles and bacteria are allowed to accumulate around the teeth and gums, inflammatory responses are triggered. As the situation escalates, plaque builds upon the teeth, eventually hardening into tartar. This biochemical chain reaction not only results in gum irritation but also creates pockets that harbor bacteria, ultimately exacerbating the condition.
On identifying gingivitis, prompt treatment is critical in averting further progression to periodontal disease. The initial approach typically involves professional dental cleaning, often necessitating anesthesia to ensure the dog is comfortable and immobile. During this procedure, the veterinarian removes tartar and polishes the teeth, making it challenging for bacteria to establish new colonies.
In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary, including excising infected gum tissue to stop the spread of infection. If bacterial infection is confirmed, an antibiotic regimen may be initiated to eliminate harmful bacteria from the mouth.
Post-treatment, veterinarians often provide dog owners with vital instructions for maintaining their pet’s dental health. This may include creating a consistent brushing schedule, utilizing vet-recommended toothpaste, and engaging in dental rinses or special formulations that target gum disease. Additionally, incorporating dental chew toys or treats can support oral hygiene by mechanically removing plaque during play.
Preventative care is paramount in ensuring that gingivitis—and its more severe implications—remains at bay. Pet owners should commit to a regular dental hygiene routine that mirrors their own, including daily brushing and periodic check-ups with a veterinarian. Such diligence not only promotes healthier gums but enhances overall quality of life for dogs.
Incorporating professional cleanings into the annual health regimen should not be overlooked. Regular veterinary visits can uncover developing issues before they become problematic, serving as a proactive approach to canine dental health.
Gingivitis in dogs is a common but preventable condition that warrants serious attention from pet owners. Recognizing the signs, understanding the underlying causes, and seeking timely treatment can protect canine companions from the unnecessary pain and complications arising from advanced periodontal diseases. Making dog dental care a priority is not merely about aesthetics; it’s a crucial aspect of overall canine health and well-being. By investing time and effort into maintaining your dog’s oral hygiene, you contribute to a happier and healthier life for your furry friend.