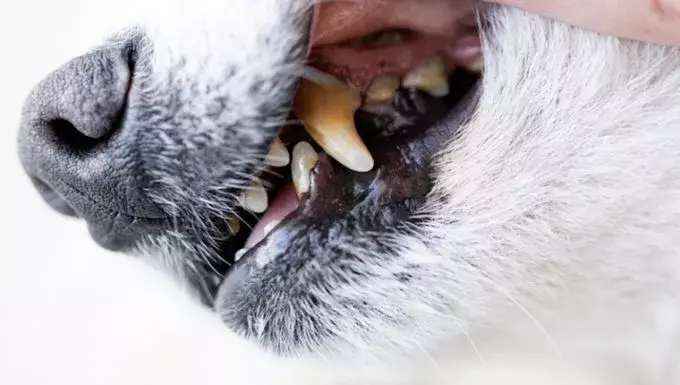
Gingival hyperplasia is a dental condition that results in the swelling and overgrowth of a dog’s gums. This ailment is not merely a cosmetic issue; if left untreated, it can evolve into serious health complications such as periodontal disease. The enlargement of the gum tissues can produce discomfort and may encourage dogs to chew or bite at their gums, which could potentially lead to further tissue damage.
If you suspect your dog might be suffering from gingival hyperplasia, it’s crucial to be observant of various symptoms that may manifest. Key indicators include:
– Swollen or inflamed gums
– Thickened gum tissue, often appearing overly pronounced
– Development of growths or excessive tissue along the gum line
– Discoloration or redness in the gums
– Formation of pockets or spaces within the gums
– Notices of bleeding, either during normal activities or when touched
These signs are essential for pet owners to recognize, as they not only indicate gum issues but could also signify an underlying disease that requires immediate veterinary attention.
All dog breeds have the potential to develop gingival hyperplasia; however, certain breeds are notably predisposed. Breeds frequently affected include Boxers, Great Danes, Dalmatians, and Doberman Pinschers. The primary culprit behind gingival hyperplasia is often a build-up of plaque and bacteria at the gum line, which triggers inflammation leading to tissue overgrowth. Furthermore, certain medications, particularly immunosuppressants, can exacerbate or induce this condition, making it crucial for dog parents to monitor their pets closely, especially if they are on long-term medication.
When faced with symptoms of gingival hyperplasia, the first step is to consult a veterinarian. A thorough examination of the mouth and teeth will typically follow, and further diagnostic tools such as X-rays or biopsies may be employed to exclude other potential conditions. If gingival hyperplasia is confirmed, surgical intervention is often recommended. This surgery can effectively remove excess tissue and clean any disease pockets, allowing for improved oral health and comfort for the dog.
Post-surgery, pain management, and strict adherence to the veterinarian’s guidelines regarding medication are critical for recovery. Additionally, it’s wise to engage in regular dental care practices, including professional cleanings and home dental hygiene routines, to prevent recurrence of gum disease and other dental issues.
Preventative care cannot be stressed enough in maintaining your dog’s oral health. Routine veterinary dental check-ups, along with consistent cleaning at home, can significantly reduce the risk of conditions like gingivitis and periodontal disease. Taking a proactive approach ensures your canine companion remains healthy, happy, and free from the burdens of dental afflictions.
As a pet owner, recognizing the signs and symptoms of gingival hyperplasia enables timely intervention, which is essential for effective treatment. By remaining vigilant and committed to your pet’s dental health, you can help ensure their overall well-being for years to come.