When it comes to canine dental health, there are many issues that pet owners need to be aware of, including a condition known as persistent deciduous teeth. This occurs when a puppy’s adult teeth emerge before the baby teeth have had a chance to fall out, resulting in a range of complications. While the medical terminology might sound daunting, it’s important for any dog owner to understand what persistent baby teeth are, the symptoms to look out for, and the treatment options available.
Most puppies begin the teething process around three months of age, at which point their baby teeth—totaling 28—start to make way for the adult set of 42 that dogs will have for the rest of their lives. The shedding of baby teeth and the emergence of adult teeth usually progresses smoothly as the puppy reaches between 14 to 30 weeks old. Persistent deciduous teeth disrupt this natural cycle, leading to several oral problems and highlighting the importance of monitoring your pet’s dental health as they grow.
Recognizing the symptoms of persistent deciduous teeth is crucial for early intervention. Typically, the symptoms center around the dog’s mouth and can encompass a variety of issues. Common signs include:
– Overbite or Misalignment: The emergence of adult teeth while baby teeth are still present can lead to dental misalignments.
– Gingivitis and Periodontal Disease: Inflamed gums often result from trapped food and bacteria due to misaligned teeth.
– Difficulty Eating: Dogs may struggle to eat due to pain or the physical barriers posed by multiple sets of teeth.
– Tooth Decay and Cavities: The presence of retained baby teeth can lead to decay, particularly if food particles get stuck in the gaps.
– Infections and Pain: Bacterial infections can develop, leading to significant discomfort for your pet.
– Jaw Development Issues: Over time, misalignment can affect the normal growth and development of the jaw.
Recognizing these symptoms enables pet owners to take proactive steps toward resolving the issue, preventing further complications.
The root cause of persistent deciduous teeth lies in the baby teeth failing to fall out as adult teeth push through. While genetics may play a significant role, certain dog breeds, particularly smaller and flat-faced varieties like Poodles, Yorkshire Terriers, and Pugs, are more susceptible to this condition. It is vital for owners of these breeds to stay vigilant as their puppies undergo teething, as early signs may be less obvious and easily overlooked.
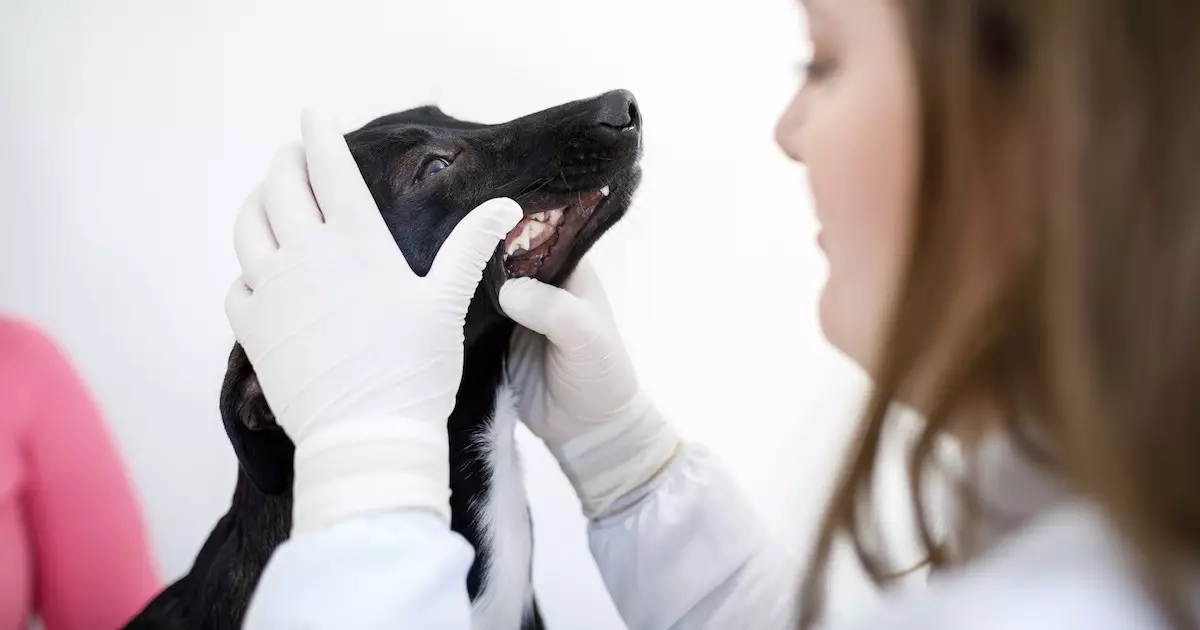
If there’s a suspicion that a puppy might be experiencing persistent baby teeth, a thorough examination by a veterinarian is essential. During this visit, the vet will conduct a physical inspection of the mouth, often supplemented by X-rays to confirm the diagnosis and assess any underlying issues related to dental structure.
The primary treatment for persistent deciduous teeth typically involves the extraction of the retained baby teeth that are not shedding naturally. This procedure generally requires general anesthesia and should be conducted by a qualified veterinarian. In some cases, if the alignment of the jaw is severely affected, additional teeth may need to be removed to ensure proper alignment.
Recovery from tooth extractions can take from a few days to eight weeks, depending on the dog’s health and age. During this recovery period, it may be necessary to alter the diet, and in some cases, a feeding tube may be recommended to ensure that the dog is receiving adequate nutrition.
Preventing complications from persistent deciduous teeth begins with diligent care. Pet owners should establish a routine of inspecting their dog’s mouth at least once a week. Regular dental cleaning is also crucial, as it helps eliminate plaque build-up and keeps the gums healthy. Early detection plays a pivotal role in mitigating the risks associated with this condition, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Understanding persistent deciduous teeth in dogs is vital for any pet owner. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and engaging with veterinary treatment options, you can significantly impact your dog’s dental health and overall well-being. Regular checks and preventative care are your best defenses against potential dental issues, leading to a healthier, happier life for your furry friend.